In the current climate of diplomatic friction between China and countries such as Japan and the United States, consumer behavior in China reveals a remarkable tendency to favor personal preference over nationalist sentiment. Despite the ruling Communist Party's efforts to stir nationalist feelings and promote propaganda condemning what it perceives as territorial infringements concerning Taiwan and Tibet, everyday purchasing decisions by Chinese consumers do not appear notably influenced by such political stances.
The Chinese state's occasional targeting of foreign companies for violating political expectations through advertising or map representations has not significantly altered consumer choices. Historical precedents of tension with Japan and the United States have seen mass calls for boycotts, street protests, and even attacks on foreign embassies and businesses. However, this wave of nationalism does not seem to steer consumer behavior notably in the present, particularly among urban middle-class and younger Chinese customers.
Jacob Cooke, CEO of Beijing-based consultancy WPIC Marketing + Technologies, highlighted that "Chinese consumers, especially those in urban middle-class and younger groups, are not basing their daily purchases on nationalist motives." This observation is evidenced in the ongoing popularity of Japanese and American products despite occasional government tensions with their home countries.
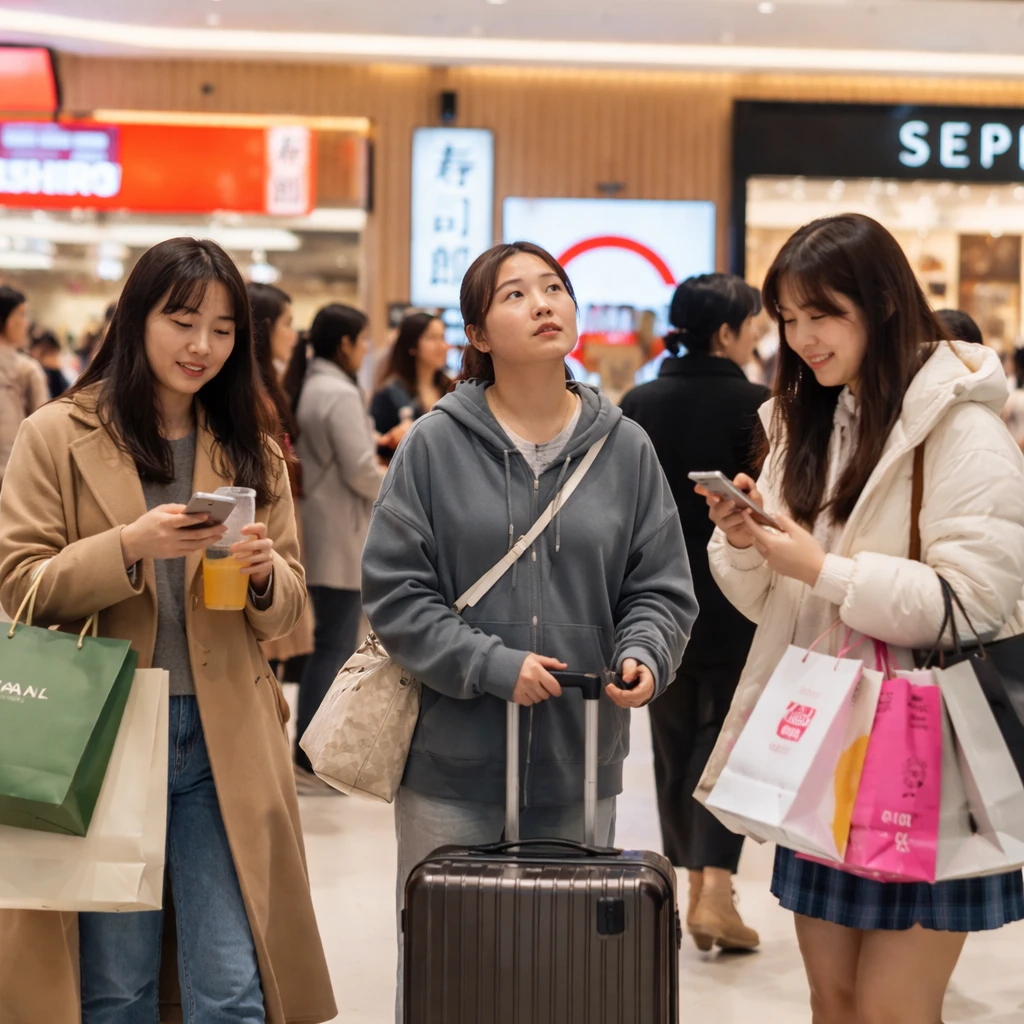
For instance, tensions arose when Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi suggested that Japan might militarily intervene if Taiwan, which China claims as part of its territory, were attacked. Beijing responded with strong condemnation and trade restrictions aimed at Japan, and government admonitions discouraged Chinese citizens from visiting the island nation, traditionally a favored travel destination. Notwithstanding these political moves, Japanese businesses continue to prosper in China as demonstrated by the grand opening of a Sushiro outlet in a Shanghai mall last December, which attracted large crowds.
Sushiro, a Japanese conveyor-belt sushi chain, has flourished since establishing its first mainland China branch in 2021. University student Edith Xiao, 23, expressed enthusiasm for the restaurant, citing the excellent taste and assured quality of ingredients. Xiao also enjoys Japanese cultural products such as the manga and anime series Chiikawa, noting no perceived impact of the political climate on her consumption of Japanese media and cuisine.
Similarly, in the realm of American culture, Chinese consumers continue to indulge despite tensions between their governments. The animated film Zootopia 2, a sequel released in 2025, has achieved extraordinary box office success in China, with revenue surpassing 4.4 billion yuan ($634 million). Fans often attend in costume, making it one of the most prominent Hollywood releases in the Chinese market.
Chinese moviegoers appreciate foreign films as a welcome diversion, especially amid the hardships imposed by COVID-19 and ongoing economic challenges, according to Shaun Rein, managing director at China Market Research Group. Rein suggests that while the Chinese government promotes local film production to build a "strong film power" by 2035, audiences still seek the enjoyment offered by international entertainment options.
In fashion, American brand Ralph Lauren has leveraged its heritage of "old money" and understated luxury to attract Chinese urban middle-class consumers who prioritize quality and brand stability over nationalist considerations. Sales of Ralph Lauren in China have grown more rapidly compared to Europe or North America, reflecting Chinese consumers' preference for offerings that meet their lifestyle aspirations rather than their country of origin.
According to Cooke, successful foreign brands in China achieve popularity not merely on nationality but by meeting genuine consumer needs or embodying desirable lifestyles. This nuanced consumer attitude aligns with the evolution of "guochao," the national trend favoring Chinese brands, which has matured to a point where consumers now feel comfortable blending domestic and foreign products based on quality and value.
Rein further notes that modern Chinese consumers have moved beyond purchasing products solely out of a sense of patriotism. Given economic uncertainties and employment concerns, choices are now predominantly driven by value and fit with personal lifestyles rather than nationalist fervor.
This shift marks a departure from previous episodes of nationalist consumer activism, such as the 2012 anti-Japan protests involving vandalism and calls to boycott Japanese products, or the 2021 backlash against Western companies like Nike linked to political disputes over minority treatment in Xinjiang. Recent controversies, like the Pokémon card event associated with a Japanese war shrine, generated critical social media reactions but did not translate into significant consumer boycotts.
Chinese consumer analyst Yaling Jiang emphasizes that expecting Chinese shoppers to uniformly follow government directives to reject foreign influences oversimplifies the situation, as geopolitics does not dictate everyday business and purchasing behavior. Instead, shoppers mix products to satisfy their personal tastes and needs.
Nevertheless, the rise of strong domestic brands presents a substantial competitive challenge to foreign companies. Chinese firms are increasingly capturing market share in sectors such as electric vehicles, smartphones, and athletic apparel by offering better value, quality, or pricing.
Government advisories urging avoidance of travel to Japan have influenced official and state-affiliated organizations, leading to cancellations of flights and group tours, and a notable 45% drop in Chinese visitors to Japan in December compared to the prior year. Despite this, many Chinese tourists continue to visit Japan individually, often discreetly limiting public social media exposure to their travels.
These factors collectively illustrate a Chinese consumer market that navigates geopolitical tensions with pragmatic purchasing habits, where personal preference and product attributes outweigh nationalist messaging.