Artificial intelligence has dramatically expanded the creation of digital content, resulting in widespread distribution of AI-produced images, videos, and music—often of varying and sometimes low quality. This surge, colloquially known as AI slop, has permeated many online spaces, raising concerns among users who seek more authentic or human-curated media experiences. Although technological and social measures are emerging to address this, fully eradicating AI slop from all digital feeds is presently considered a daunting, if not impossible, task. Henry Ajder, an expert advising on AI and deepfake issues since 2018, likens the challenge to avoiding industrial-era smog before pollution controls existed, indicating pervasive difficulty in completely filtering such content from everyday user experiences.
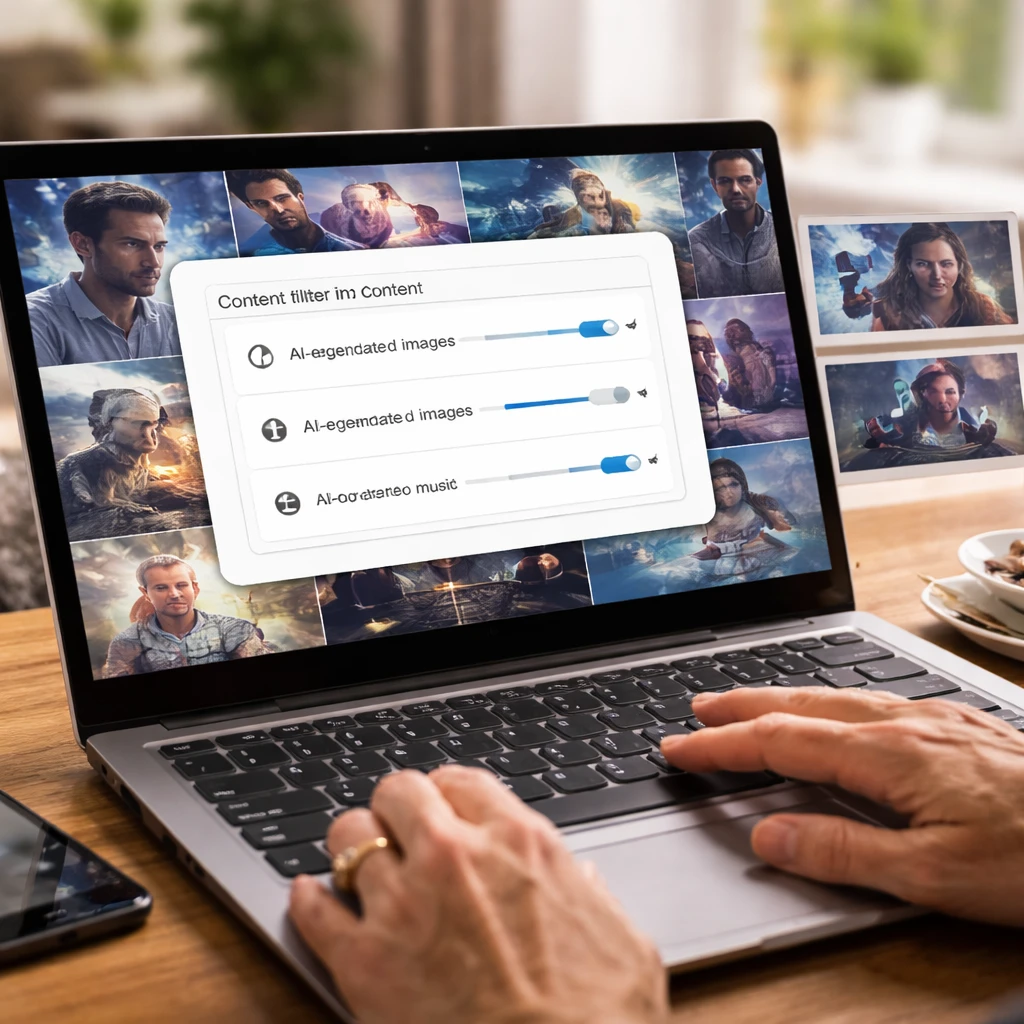
Among platforms grappling with this influx is Pinterest, which initially gained prominence as a repository for thematic inspiration, but has seen its feeds increasingly populated with AI-generated material. In response, Pinterest introduced a "tuner" feature allowing users to calibrate the presence of AI content in their personal feeds. Initially deployed on Android and desktop browsers with gradual rollout on iOS, the tool targets categories prone to AI modification—such as beauty, art, fashion, and home décor—enabling users to opt for more human-centric content. Subsequently, the feature expanded to encompass additional categories including architecture, entertainment, health, sports, food, and drinks. Users can access the tuner by navigating to Settings, selecting "refine your recommendations," and adjusting toggles under "GenAI interests" to specify categories for reduced AI content.
Short-video platform TikTok is a particularly fertile ground for AI-generated videos, with the company acknowledging that at least 1.3 billion clips on its service carry AI-generated labels. As part of its ongoing efforts, TikTok announced plans to test a feature that grants users greater influence over AI-generated content appearing in their "For You" feeds, although the timing of broad deployment remains uncertain. Users may find these controls within the mobile app by accessing Settings, then Content Preferences, followed by Manage Topics, where sliders adjust content types ranging from dance to nature—and potentially AI-generated material. Additional access exists through the For You feed via post-specific menus. However, such options are unavailable on the desktop site, and TikTok emphasizes that these controls modulate content exposure rather than eliminating AI-generated posts entirely. This tailoring approach allows enthusiasts of AI-generated history content, for example, to receive more of it, while others can reduce its presence.
In the realm of music streaming, AI-generated songs have surged due to tools like Suno and Udio, which produce polished tracks from simple textual input. This proliferation presents challenges for music platforms contending with accounts posting synthetic music under false artist names. Among these services, Deezer, a smaller Europe-based streaming company, stands out for its approach of labeling AI-generated tracks to help listeners identify them. Deezer reports daily uploads of roughly 60,000 AI-produced songs, comprising over 39% of total daily uploads, and has flagged more than 13.4 million AI tracks since last year. The platform cites financial motives behind the practice, specifically attempts to generate revenue through fraudulent streaming.
For users seeking to avoid AI-generated media altogether, alternatives to mainstream Big Tech platforms are emerging. Cara, a platform focused on artist portfolios, prohibits AI-generated creations outright. Pixelfed, an Instagram alternative devoid of advertisements, offers communities like one devoted to art that does not permit AI content. The Spread platform appeals to audiences wishing to engage more deeply with human-generated ideas amidst the growing AI content volume. Anticipated additions include diVine, a new social media app inspired by the former Vine service. Currently in limited prerelease for iOS, diVine markets itself with a "No AI Slop" promise, leveraging various detection methods to filter AI media. An Android beta is forthcoming, with plans for a full launch delayed to accommodate unexpectedly strong demand.
Tackling the proliferation of AI-generated content poses ongoing challenges for both platforms and users, as tools to modify consumption patterns develop gradually. While new features aim to balance user preferences and content discovery, the inevitability of exposure to some AI-produced media remains, driven by the volume, ease of creation, and evolving platform policies. This dynamic suggests a period of adjustment as the digital ecosystem negotiates the coexistence of human and AI-generated content.
Among platforms grappling with this influx is Pinterest, which initially gained prominence as a repository for thematic inspiration, but has seen its feeds increasingly populated with AI-generated material. In response, Pinterest introduced a "tuner" feature allowing users to calibrate the presence of AI content in their personal feeds. Initially deployed on Android and desktop browsers with gradual rollout on iOS, the tool targets categories prone to AI modification—such as beauty, art, fashion, and home décor—enabling users to opt for more human-centric content. Subsequently, the feature expanded to encompass additional categories including architecture, entertainment, health, sports, food, and drinks. Users can access the tuner by navigating to Settings, selecting "refine your recommendations," and adjusting toggles under "GenAI interests" to specify categories for reduced AI content.
Short-video platform TikTok is a particularly fertile ground for AI-generated videos, with the company acknowledging that at least 1.3 billion clips on its service carry AI-generated labels. As part of its ongoing efforts, TikTok announced plans to test a feature that grants users greater influence over AI-generated content appearing in their "For You" feeds, although the timing of broad deployment remains uncertain. Users may find these controls within the mobile app by accessing Settings, then Content Preferences, followed by Manage Topics, where sliders adjust content types ranging from dance to nature—and potentially AI-generated material. Additional access exists through the For You feed via post-specific menus. However, such options are unavailable on the desktop site, and TikTok emphasizes that these controls modulate content exposure rather than eliminating AI-generated posts entirely. This tailoring approach allows enthusiasts of AI-generated history content, for example, to receive more of it, while others can reduce its presence.
In the realm of music streaming, AI-generated songs have surged due to tools like Suno and Udio, which produce polished tracks from simple textual input. This proliferation presents challenges for music platforms contending with accounts posting synthetic music under false artist names. Among these services, Deezer, a smaller Europe-based streaming company, stands out for its approach of labeling AI-generated tracks to help listeners identify them. Deezer reports daily uploads of roughly 60,000 AI-produced songs, comprising over 39% of total daily uploads, and has flagged more than 13.4 million AI tracks since last year. The platform cites financial motives behind the practice, specifically attempts to generate revenue through fraudulent streaming.
For users seeking to avoid AI-generated media altogether, alternatives to mainstream Big Tech platforms are emerging. Cara, a platform focused on artist portfolios, prohibits AI-generated creations outright. Pixelfed, an Instagram alternative devoid of advertisements, offers communities like one devoted to art that does not permit AI content. The Spread platform appeals to audiences wishing to engage more deeply with human-generated ideas amidst the growing AI content volume. Anticipated additions include diVine, a new social media app inspired by the former Vine service. Currently in limited prerelease for iOS, diVine markets itself with a "No AI Slop" promise, leveraging various detection methods to filter AI media. An Android beta is forthcoming, with plans for a full launch delayed to accommodate unexpectedly strong demand.
Tackling the proliferation of AI-generated content poses ongoing challenges for both platforms and users, as tools to modify consumption patterns develop gradually. While new features aim to balance user preferences and content discovery, the inevitability of exposure to some AI-produced media remains, driven by the volume, ease of creation, and evolving platform policies. This dynamic suggests a period of adjustment as the digital ecosystem negotiates the coexistence of human and AI-generated content.